week04
Memory Forensics
Questions?
Whoami
- Jesse Merhi (Like that herb + “he”)
- Product Security @ Atlassian
- I like hacking and AI/machine learning, talk to me about them.
In saying that..
- If any of you want some advice regarding career things, then…
how to contact me
- Me: [email protected]
- Admins are: [email protected]
- @Merhi on the SecSoc Discord (pls join)
- https://secso.cc/discord
Admin Things
- Reminder Report 1 is due this Sunday
- Also Week 4 and 5 challenges are now out (both due end of Week 5 / 19th October)
Memory
- Not everything is stored on a disk
- Why
What’s in the memory
- Application data
- The application itself
- Operating system data
- Networking data
Memory Forensics
- We can find remnants of data in memory
- Some malware never touches the disk
What could you find in memory?
- Recently executed commands
- Running processes, and their code / library
- Drivers & daemons
- Passwords, keys, security stuff
Why?
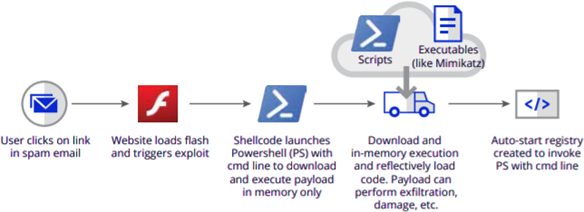
Fileless Malware
- Even if it never touches the disk…
- … at some point, it has to be in memory
- Process Hollowing
- When a legitimate process is paused, duplicated, and its executable memory is replaced with malicious code
- This can bypass simple AVs which ignore whitelisted/trusted services
Collecting memory dumps
- RAM is volatile, you can’t capture it after the computer is shutdown*
- It can be hard to collect when it’s live
- You don’t want to change the machine’s state
When is collecting memory difficult?
- Machine is in data center / cloud
- How would you collect it?
- Computer is locked and you don’t know the password
- Known user isn’t an administrator
What processes are sus ඞ
Obfuscate names/paths (drop some malware in a system location and give it a legitimate name) Misspelled versions of proper system processes Proper process names in wrong location Duplicate processes that should only spawn once Processes that have a parent when they shouldn’t System processes with start time much later than boot-time System processes running under a user account
Volatility
RAM is volatile
Reference list
- Command list can be found here
- HackTricks
List all the processes
windows.pslist- Get process list (from
EPROCESS)
- Get process list (from
windows.pstree- Get processes tree (from
EPROCESS)
- Get processes tree (from
windows.psscan- Byte-scan of the process entry memory region
- Can get hidden processes (malware???)
Dumping a process
windows.dumpfiles --pid <PID>- get the executable & DLLs
windows.memmap --dump --pid <PID>- get all memory resident pages
windows.dllist --pid <PID>- list the DLLs used by a process
See how a process was started
windows.cmdline- shows the arguments used for the process
windows.envars [--pid <pid>]- display process environment variables
windows.handles --pid <pid>- show files, threads, etc a process has opened
Registries
windows.registry.hivescanwindows.registry.hivelistwindows.registry.printkey -K "Path\To\Key"
Viewing files
windows.filescanwindows.dumpfileswindows.dumpfiles --virtaddr <o>windows.dumpfiles --physaddr <o>
Networking
windows.netscanwindows.netstat
Pattern match strings
windows.strings --strings-file ./strings_filewindows.vadyarascan --yara-rules "https://" --pid <PIDS>yarascan.YaraScan --yara-rules <R>
Dumping hashes
windows.hashdump- grab common windows hashes (SAM+SYSTEM)
windows.cachedump- grab domain cache hashes inside the registry
windows.lsadump- grab LSA secrets